Stroke Symptoms — Recognise Early, Act Fast
BE-FAST Quick Guide

Balance
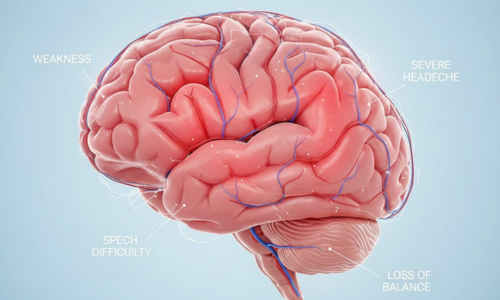
Sudden loss of balance or coordination

Eyes
Blurred or loss of vision in one/both eyes

Face
Face Face drooping on one side

Arm
Weakness or numbness in an arm/leg

Speech
Slurred or confused speech

Time
Seek emergency care immediately
Ischemic vs Haemorrhagic Stroke Symptoms
🩸 Ischemic Stroke (Clot)
- Numbness or weakness on one side
- Difficulty speaking
- Trouble walking
- Sudden vision problems
⚠️ Haemorrhagic Stroke (Bleed)
- Sudden severe headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Sudden confusion or disorientation
Are You Seeing This?
What To Do Immediately
Call Emergency Number Immediately
Seek urgent medical help without delay.
Note the Time Symptoms Started
This helps doctors decide the best treatment.
Don't Give Food, Water or Medicine
Wait for medical guidance before giving anything.
Frequently Asked Questions
Many strokes—especially ischemic strokes—can occur without pain.
Symptoms like weakness, numbness, speech difficulty, or vision changes may appear suddenly even if there is no headache or pain.
A painless stroke is still a medical emergency.
Yes, women may experience additional or subtle symptoms, including:
Sudden fatigue
Confusion or disorientation
Fainting
Nausea or vomiting
Hiccups
Shortness of breath
Sudden behavioral changes
A TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) is a temporary blockage of blood flow in the brain.
Symptoms may:
Appear suddenly
Last a few minutes to an hour
Completely resolve on their own
BUT—TIAs are serious warning signs.
Chronic stress increases blood pressure, inflammation, and unhealthy habits (smoking, poor sleep), all of which raise stroke risk.
Strokes can occur at any age, even in the 20s–40s.
Causes in young adults include:
Heart rhythm problems
Blood clotting disorders
Neck artery tears
High blood pressure
Smoking and drug use
Autoimmune diseases
No, Some strokes only affect speech, vision, memory, or balance.
Even small strokes without paralysis still require immediate treatment.
Some strokes progress over minutes to hours (called “stroke in evolution”).
Any worsening signs should be considered an emergency.
Yes, dehydration can increase blood thickness, making clot formation more likely—especially in older adults.
Common conditions that mimic stroke:
Migraines
Seizures
Low blood sugar
Vertigo
Infections
Medications causing drowsiness
When in doubt, treat it as a stroke.
Immediately — ideally within the first 60 minutes.
Earlier treatment improves recovery and reduces disability.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
Fast Stroke Action
Consistently high blood pressure damages blood vessels, greatly increasing stroke risk.
Diabetes
High blood sugar gradually harms arteries, making the brain more vulnerable.

Smoking
Smoking narrows blood vessels and speeds clot formation, raising stroke chances.

High Cholesterol
Excess cholesterol creates artery blockages that can restrict blood flow to brain.

Previous Stroke / TIA
A past stroke or mini-stroke strongly increases the likelihood of another.

Heart Disease
An irregular heartbeat or weak heart can produce blood clots, which may travel to the brain.

Obesity
Being overweight often leads to high BP, diabetes, and higher stroke risk.

Age Above 55
Stroke risk rises significantly after 55 as blood vessels naturally weaken.
